Many individuals and companies are coming up with new mobile app ideas to make it big in their field. They either want to reach a new audience or better serve their existing customers.
However, people are relatively unaware of the steps or processes needed to turn a mobile app idea into reality. Due to a lack of expertise and information among startups and established companies, most of them don’t know how to go about shaping the app idea.
Simpalm is a leading mobile app development company in USA, helping several startups and non profits build their mobile apps. Here are the 10 key steps I have followed in our 12 years of experience. I believe that my list can help anyone from any industry get their mobile app idea turned into reality.
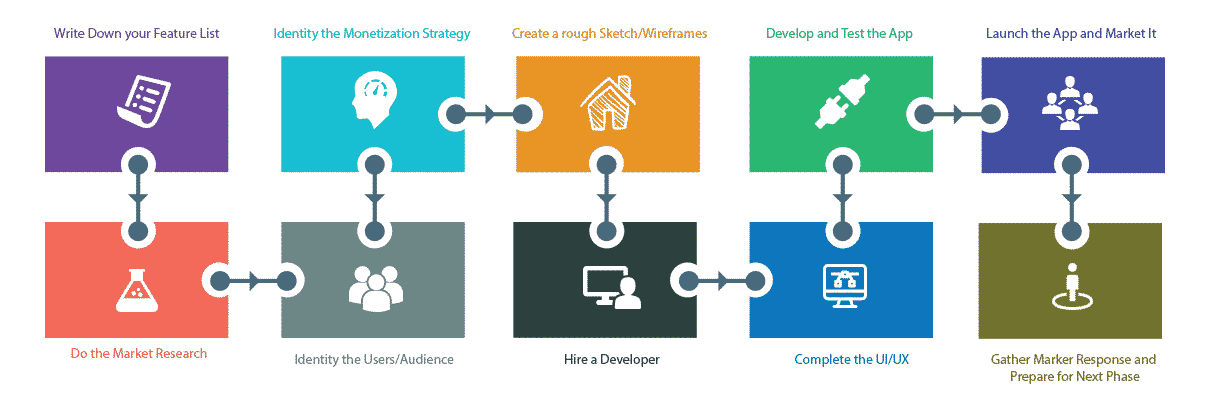
Step 1: Write down your feature list
Conceptualize your idea begins by taking some notes. Before doing anything, you should write whatever comes to your mind. Writing down the feature list on a piece of paper helps you focus on your idea and expand on it. I recommend writing your idea several times and in many different ways. This list also will be helpful when you have a discussion with your co-founders, designers, investors or developers; they all are going to ask for it. Note that you should have them sign an NDA before you share your feature list. Your feature list should be clean and easy to understand. Also make sure it has popular and unique features, which will play a major role in the success of your product.
Read More: How to Create a Mobile App RFP
Step 2: Do market research
After writing your strong list of features, you want to do market research to identify the competition, trends and market needs. Make sure there are no similar apps in the market. If there are, find out their reviews, ratings, feedback, and what is missing in them. Add features in your app that would make it unique and more attractive to the audience. After doing market research, you should update your feature list.
Step 3: Identify the users/audience
It is very important to identify who would use your app and who the audience would be for your product. Your users can be from a particular industry, gender, region, age group, existing customers, income group, specific profession, or any other group. Once you identify some demographics about the audience, you can find out what people from these demographics prefer or like. Knowing your audience helps you re-engineer your app and the features in it to cater to them. Your whole project moves around user engagement. You can also conduct focus group studies to find out what your audience may like or dislike. Your audience will decide your product’s success, and this insight from a focused study can go a long way in defining product success.
Step 4: Identify the monetization strategy
Making money is the biggest reward and energizer for your idea. You can make money from your app idea in several ways: subscription fee, in-app purchase, in-app ads, user data, sponsorship. You want to know which one works for your app, audience, and market. Launching a paid app does not work these days, but you can make the app free with an in-app purchase option for additional functions. In-app ads are also losing their shine these days due to user experience. Having user data is becoming a big monetization technique, as you can use it to make indirect money. You can find sponsorship for the app; this works for an app with a social mission. It is important for you to select 1 or 2 techniques that would give you a good return on investment.
Step 5: Create a Rough Sketch/Wireframe
You may not have done it before, or may not know how to do it. However, the rough sketch or wireframe helps you define the concept and refine the requirements of your product. You can draw a rough sketch using paper and pencil, while a wireframe can be created using online tools. When you start doing the sketch/wireframe, you will be able to polish your app idea and features list further. Also, this helps you decide the appropriate navigation of the whole application. You don’t need technical skills for this step, but you need to have a common-sense understanding of how navigation works. Your wireframes, along with your feature list, will create very good specifications for you to build the mobile app.
Step 6: Approach Local Mobile App Developers and Get Estimates
Once you have your initial version of the feature list and wireframe, you want to start identifying vendors who can build your mobile app in a high-quality, cost-effective way. You should search for local vendors and some global vendors and reach out to them. Once you shortlist 5 to 6 good vendors, have them sign the NDA and send them the project details. A good vendor should evaluate your details and ask you lots of questions. You should make sure to answer them in detail so that your idea is fully communicated. A good vendor should also be able to provide you some suggestions to improve your idea. You should get proposals from multiple vendors, with time and cost for development, and compare them. You should evaluate the vendors on past performance, process, price, time, testimonial and their eagerness to work for you. Finally, you should be able to select one vendor and start working with them.
Step 7: Complete the UI/UX
Once you have selected the company, you should work with them to create the UI/UX of the app. You should have them first create the detailed wireframe of the application so that you can visualize each screen, function and flow of the application. After review, you can decide to add or remove features. Once the wireframe is done, you want them to create the visual design of the application. It should give the color, theme, fonts and visual appeal for your idea. This step will give you a near-final picture of what your mobile app would look like and how it would flow. After completing it, have your vendor reevaluate the development plan, time and cost. If the initial estimate of time/cost has increased, get more funding or reduce some of the features. You want to pay the right value to your mobile app developer.
Step 8: Get the App Developed and Tested
Have your app developer start building the app for you. They should be able to send you the app (in progress) every week and you should be able to test and give them feedback. It is very essential for you to QA the app as they develop it, as this helps you control the quality, cost and timeline, and learn whether the mobile app needs some tweaks. You can involve your friends in the testing as well. If you come up with new sets of features during the development, discuss those with your app developer and get the time and cost estimate. If it fits your budget, get it done right away. If not, wait for the next phase.
Step 9: Launch the App and Market It
Once you are satisfied with the app, launch it in the iTunes App Store and Google Play Store. You should also start marketing the app. Get some consulting from experts on app marketing. You can also do self-marketing. Start on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram, as this is an easy way to spread the word about the app. You should also reach out to reporters and bloggers who may be interested in your app and write about it. A press release on free sites or a paid site can be very handy. If you have more in your budget, you can hire a PR or app marketing company.
Step 10: Gather Market Response and Prepare for the Next Phase
After the initial launch and marketing, you can collect user data, market response, and demand. If you receive a good response, you can plan the next phase for the app. Repeat Step 1 through 9 for the next phase. This time, you should be able do them a lot faster and more efficiently. If the app is not received well in the market, find out what is hampering growth and have a plan of action.

 App Development
App Development Web Engineering
Web Engineering AI Services
AI Services Startups
Startups Health / Fitness
Health / Fitness Education
Education Social
Social Nonprofit
Nonprofit Fintech
Fintech Logistics
Logistics Government
Government HR Software
HR Software About Simpalm
About Simpalm Our News
Our News Client Testimonials
Client Testimonials Careers
Careers Awards
Awards Resources
Resources Information
Information



One Response to 10 Key Steps to Turn Your Mobile App Idea into Reality